Over the past week, I have been thinking about Walmart selling its entire JD.com stake unexpectedly. The implications of this decision have not been described adequately, nor have the future impact been discussed. What are the consequences for both Walmart and JD.com?
This story started in 2011 when Walmart made an undisclosed minority investment in Yihaodian. In 2015, Walmart acquired the remaining shares in the e-commerce platform Yihaodian for an undisclosed amount. It is important to note that in June 2015, the Chinese government started allowing total foreign ownership of some e-commerce businesses. This decision was to encourage foreign investment and competition in the e-commerce sector. In 2016, Walmart sold Yihaodian to JD.com and acquired 5% of JD.com stock at a valuation of $1.5B. The company also started a strategic partnership with JD.com.
The strategic partnership included:
- JD.com will acquire the Yihaodian marketplace platform assets, including the brand, website, and app. At the same time, Walmart will continue to operate the Yihaodian direct sales business and sell products in the marketplace.
- Sam’s Club China plans to open a flagship store on JD.com, expanding its high-quality imported products availability in China, offering same- and next-day delivery through JD.com’s nationwide warehousing network.
- Walmart and JD.com are partnering to enhance product selection across China by leveraging their supply chains and expanding the range of imported products.
- Walmart will be listed as a preferred retailer on JD.com‘s O2O JV Dada, boosting online traffic and allowing customers to order fresh food and items for 2-hour home delivery while maintaining its physical stores.

Source: Walmart
New joint initiatives between the companies in 2016
The companies jointly launched three new initiatives:
- Walmart is set to launch an exclusive Sam’s Club flagship store on JD.com, offering customers access to premium, quality products with same- and next-day delivery. Walmart will use JD.com’s nationwide logistics network to stock Sam’s Club merchandise in JD’s warehouses, aiming to expand its Sam’s Club presence to 20 more locations by 2019. JD.com users can buy Sam’s Club products at membership prices for a 10-day introduction period.
- On JD Worldwide, a cross-border platform, Walmart launched a Walmart Global store offering Chinese consumers a wide range of high-quality products imported worldwide. Walmart plans to expand and add new categories as it connects items from other markets to China, delivered through JD’s last-mile logistics network.
- New Dada, a joint venture with JD.com, has launched a two-hour delivery service for customers ordering from over 20 Walmart stores in select cities. The service is expected to double by the end of the year. The partnership follows the merger of Dada and JD Daojia, China’s largest crowdsourced logistics platform, in April 2016.
During 2015 and 2016, Chinese e-commerce was dominated by Alibaba’s Taobao, Tmall, and JD.com. Retailers such as Walmart, the UK’s Tesco, and France’s Carrefour had their marketshare impacted by local retailers for over five years. Walmart decided that the best way forward for its Yihaodian asset would be a part of JD.com and to become a shareholder. Walmart realized that to be found in China, it had to be on JD.com platforms to grow its businesses with new Chinese consumers who would be shopping via shopping apps rather than visiting stores.
It would be incomplete to mention that this period saw a growing Chinese economy and, in some cases, becoming consumption-driven.
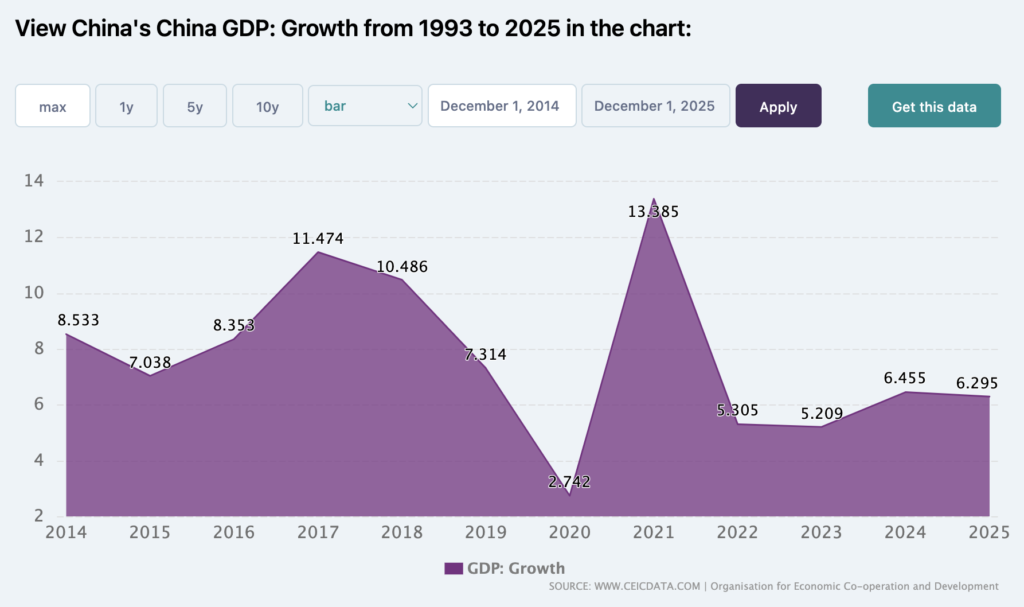
Source: CEIC
No one counted on the emergence of new platforms, such as Pinduoduo, which connects manufacturers with customers and focuses on lower-tier Chinese cities that were not serviced by Alibaba and JD.com. We had the emergence of platforms such as Douyin (called TikTok outside of China) and Kuaishou, which used short videos and livestreaming to take marketshare away from Alibaba and JD.com. Alibaba invested significantly in livestreaming to help customers find Taobao sellers and products selling local products.
It is important to note that the Chinese government has managed the e-commerce sector better than any other region and kept these companies on short leashes. It fined Alibaba in 2021 a record amount for anti-competitive behavior. It also called for open ecosystems to ensure that consumers could interact more easily with different platforms without blocking between apps and businesses.
So Why Did Walmart Sell Its Entire Stake in JD.com?
Walmart’s membership retailer, Sam’s Club, has remained the market leader in China for warehouse retail. Over eight years, its strategic partnership with JD.com has helped the company gain customers without additional digital marketing. Chinese consumers had access to flagship stores on JD.com platforms, which were marketed aggressively by the Chinese platform. That is marketing that cannot be bought on any platform in China.
Sam’s Club has become Walmart’s innovation platform. To look at Walmart’s future, visit a Sam’s Club. The membership model depends on annual fees and does not sell items with large markups. These lower margins are further squeezed when accessed by a third party. Sam’s Club China grew membership with consumers due to access to JD.com platforms for an introductory period. Buying a membership after experiencing a platform is more accessible for customers after the experience. Why would consumers buy a membership without experiencing Sam’s Club?
Chinese e-commerce has become a low-price battleground between Alibaba, JD.com, and Pinduoduo. The platforms are all growing slower as Chinese consumers benefit from multiple platforms that aggressively market promotions to them. Why would Walmart keep Sam’s Club on JD.com if the platform grows at less than 5% annually? I believe that most Chinese marketplaces are growing at one percent.
This may sound trivial, but Walmart now has a deeper e-commerce understanding and experience than in 2015 and 2016 when it partnered with JD.com. Most multinational businesses want to be in China, but Chinese retail is unlike any market worldwide, as e-commerce has frog-leaped retail. Using digital platforms and marketplaces was the only way to grow in China. In 2024, brands will be less likely to join Chinese marketplaces due to competition with local brands and the high costs associated with their use. Did Walmart have China envy when it invested in Yihaodian in 2011? Likely.
JD.com has provided Walmart and Sam’s Club with access to its logistics/supply chain to ensure that goods can be quickly shipped to customers. However the inventory needed to be in JD.com warehouses which goes against Walmart’s current logistics strategy of fulfillment from stores. The question no-one is asking is how does the last-mile look for Sam’s Club and Walmart customers? Yihaodian has access to 250 delivery hubs that enables quick delivery of groceries in 200 Chinese cities. I cannot believe that Sam’s Club and Walmart China would not build a supply chain that enables delivery of goods.
Walmart’s $3.6B return on their JD.com investment will likely we invested in Chinese ventures that will provide better return versus having a third-party partnership with a marketplace/ online retailer.
What is at stake for JD.com?
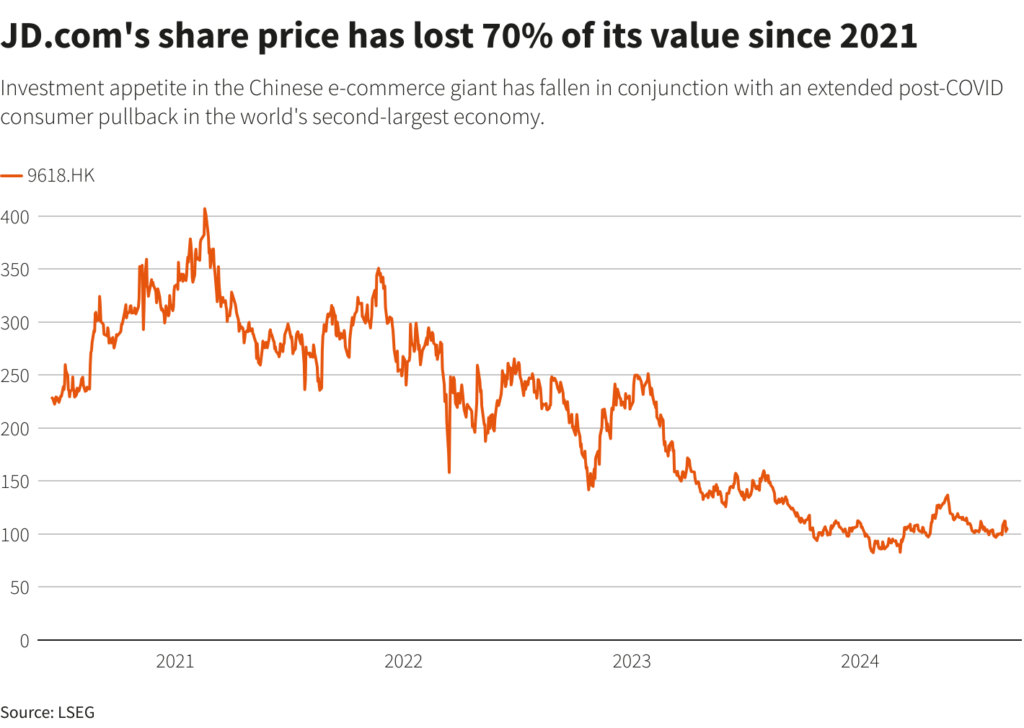
Source: Reuters
JD.com has invested in supply chain infrastructure and has seen overhead increase due to having over 519k staff of which 355k works for its logistics business. jD.com has lost its largest shareholder in Walmart and will need to convince investors that it can grow amid competition with Alibaba and Pinduoduo.
The company has dabbled with an international marketplace to help Chinese manufacturers reach international customers without real impact. They are unable to compete with AliExpress, Temu, TikTok Shop and Shein as they have invested and grown internationally to markets. Cross-border e-commerce should fit JD.com but its retailer business model will negatively impact selection and relevance outside China.